Faraday Measuring Station
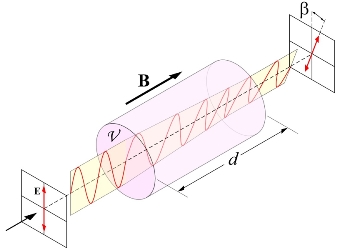
A characteristic feature of magneto-optically active materials is their Faraday rotation, which can be measured with a Faraday measuring station. During a Faraday measurement, the field strength is tuned in a defined way and the intensity of the measuring light is continuously detected. The direction of the magnetic field and the propagation direction of the light in the sample are parallel to each other and thus perpendicular to the layer plane or parallel to the sample axis (Polar Faraday Effect). The result is a magneto-optical hysteresis loop - the Faraday characteristic.
Application examples:
- Typical magneto-optical materials include garnet layers (BIG, YIG), Faraday insulators (TGG) and magneto-optical glasses (Tb-doped glass)
- Measurement of the Faraday rotation of layer systems (substrate with layer) and volume material
- Determination of the specific Faraday rotation
- Measurement of magneto-optical hysteresis loops
- Determination of the Verdet constant
Device configuration:
- Faraday rotation in transmission and reflection
- Typical wavelengths of LEDs: 505 nm, 530 nm, 590 nm, 630 nm
- Specimen thickness: 0.5 to 20 mm (typ.)
- Sample size: 10 to 100 mm (rectangular), 1 to 4 inches (round)
- Resolution Faraday rotation angle: 1°/T
- Field strength range: 0.1 to 500 mT (typ.)
- Measuring surface: smaller than 10 mm²
- Measuring temperature: RT (23°C)
- Automatic recording of Faraday curve and CSV output
- No account taken of the elliptical component

Download Faraday measuring
Other Measuring Instruments
- AMR Magnetometer
- Fluxgate Magnetometer
- Hall Magnetometer
- NMR Magnetometer
- Electromagnet
- Coil Systems
- M-axis
- HyMPulse
- Rotor Measuring Station
- Magnetic Mapping
- MagHyst
- Impedance Measuring Station
- Vibration Magnetometer
- HF Measurement Technology
- Network Analyzers
- Faraday Measuring Station
- Prism Coupler
- Gonioreflectometer
- Form Measuring System
- Coordinate Measuring Machine
- Twist Tester
- CPU Cluster
- GPU Cluster
Manufacturer:
INNOVENT





