Fluorination
Gas phase fluorination is an innovative and practically applicable process for durable modification of polymer surfaces. In contrast to coating technologies, the surface is not coated, but modified. While the adhesive forces in coatings are mostly in the range of the van-der-Waals force, stable fluorine compounds are formed during treatment with fluorine gas.
Depending on the process parameters, fluorination can influence various surface properties. A distinction is made between fluorination without oxygen, and with oxygen (oxy-fluorination).
The process can modify the following surface properties:
- Permanent hydrophilic
- Long-lasting activation of non-polar surfaces (for improved adhesion)
- Improved barrier against fuel and gas permeation
- Reduced friction for elastomers and TPE
- Reduced migration of polymer additives
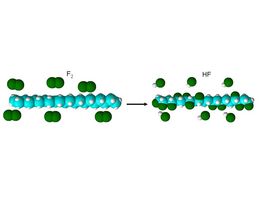
The surface is modified through the reaction of fluorine gases, which strongly react with hydrogen containing substances, thereby forming hydrogen fluoride. The free functional sites can react with fluorine, oxygen, or by crosslinking the polymer. Calcium carbonate absorbs hydrogen fluoride and residual fluorine to protect operators and the environment.
A special advantage of the gas phase fluorination is the efficient treatment of complex geometries. Even the surfaces in holes and undercuts are treated completely and homogeneously.
INNOVENT has a close cooperation with users, contract treatment companies, and the equipment construction company Fluor Technik System GmbH.

Dr. Tina Toelke
Surface Technology
Team Leader
Chemical Technologies
e-mail
Phone: +49 3641 282554